OUR PCBS
Rigid-flex PCB
TopFast provides Rigid-flex PCB services tailored to meet customer’s needs. Full design support, fabrication, layout optimization, and assembly. Ensure that your Rigid-flex PCBs are manufactured to the highest standards, using the most advanced technologies.
You'll like it.
-
Rogers PCB
-
High Frequency PCB
-
High Sepeed PCB
-
2 Layer Board
-
4 Layer Board
Rigid-flex PCB
Characteristics &Manufacturing
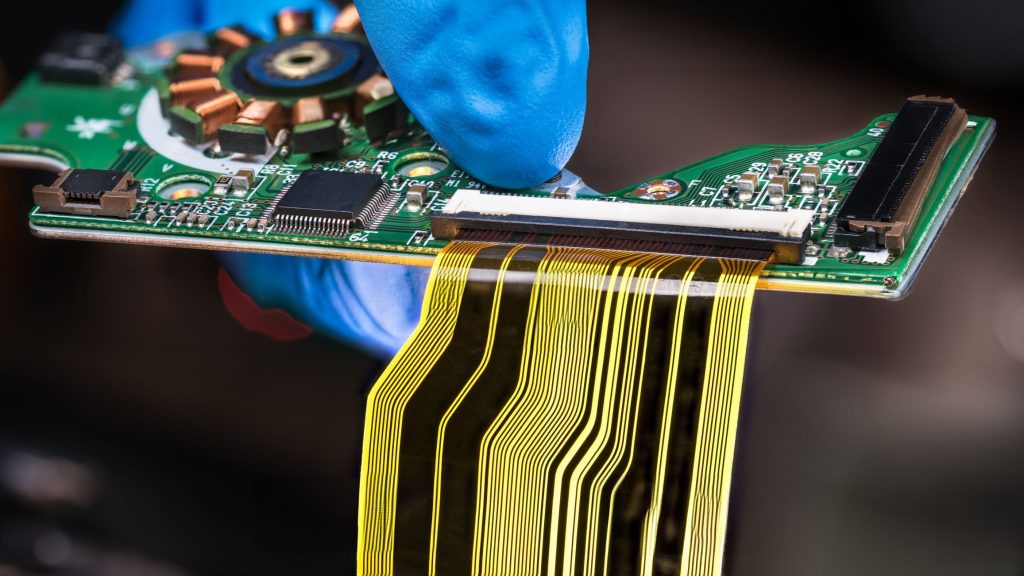
Introduction to Rigid-flex PCB
Flexible Printed Circuit Boards (FPCBs) are electronic circuit boards made from flexible substrates. They are designed to adapt to various spatial requirements by allowing bending, folding, and flexing. FPCBs are composed of metal foils, such as copper, and flexible polymers like polyimide. These boards are known for their lightweight, flexibility, high-temperature resistance, and excellent bending capabilities.
Manufacturing Process of Rigid-flex PCB
-
01
Material Selection
Suitable rigid materials and flexible materials are selected for the Rigid-flex PCB. Rigid materials commonly used include glass fiber reinforced resin (FR-4), while flexible materials often include polyimide (PI). The material selection is closely related to the application environment and requirements.
-
02
Material Preparation
The selected materials undergo pre-processing, such as impurity removal, thickness control, and uniformity. This ensures that the materials meet the required quality and performance.
-
03
Rigid Area Fabrication
Conventional rigid PCB manufacturing processes, including lamination, photolithography, etching, drilling, etc., are used to fabricate the circuit layers in the rigid area.
-
04
Flexible Area Fabrication
Specialized flexible PCB manufacturing processes, involving steps such as lamination and etching, are used to form the flexible circuit layers. Flexible circuit layers typically employ thin-film materials like polyimide (PI).
-
05
Rigid-Flex Connection
The rigid area and flexible area are interconnected. Common methods include the use of adhesives, copper foils, and solder pads.
-
06
Surface Treatment
Chemical treatment or metallization is performed to form reliable conductive layers on the surfaces of the circuit layers in the rigid and flexible areas. This enhances the reliability and performance of signal transmission.
-
07
Panelization and Processing
The Rigid-flex PCB is cut into the desired shape and size according to design requirements through processes such as cutting, drilling, and bending.
-
08
Component Assembly
Electronic components and connectors are mounted on the Rigid-flex PCB using techniques such as soldering or adhesive bonding.
-
09
Testing and Validation
Electrical testing, signal integrity analysis, and validation are performed on the completed Rigid-flex PCBs to ensure they meet the requirements of combined rigid and flexible applications.

